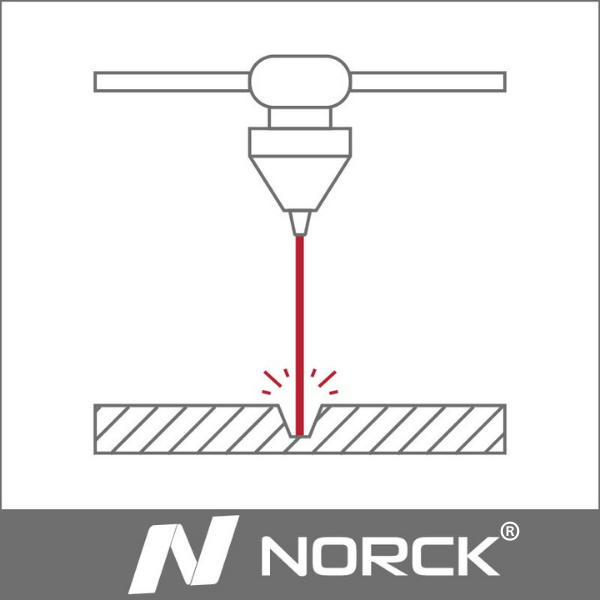
Wear describes the loss of material of a part due to mechanical, thermal, or chemical interactions. Wear-resistant parts are mechanical components that resist wearing. Wear is often due to friction between parts such as cutting blades, gears, bushings, and bearings.
In many cases reducing the friction reduces the wear of parts which can be done by:
• Choosing materials with a lower friction coefficient
• Heat-treating surfaces to make them more rigid
• Using lubrication
Wear-resistant custom parts can be made or fabricated using several fabrication methods, and they are used in the following sectors:
- Medical: surgical tools, implants, and orthopedics.
- Industrial: Welded structures, gears, shafts, jigs and fixtures, and enclosures.
- Hardware: Hinges, handles, tools, screws, nuts, and rivets
- Aerospace & Automotive: Bodies of aircraft and cars, electrical cables
- Robotics: Robots' bodies, gears, shafts, grippers
- Consumer products: home appliances, cooking utensils, PC enclosures, jewelry


 English
English