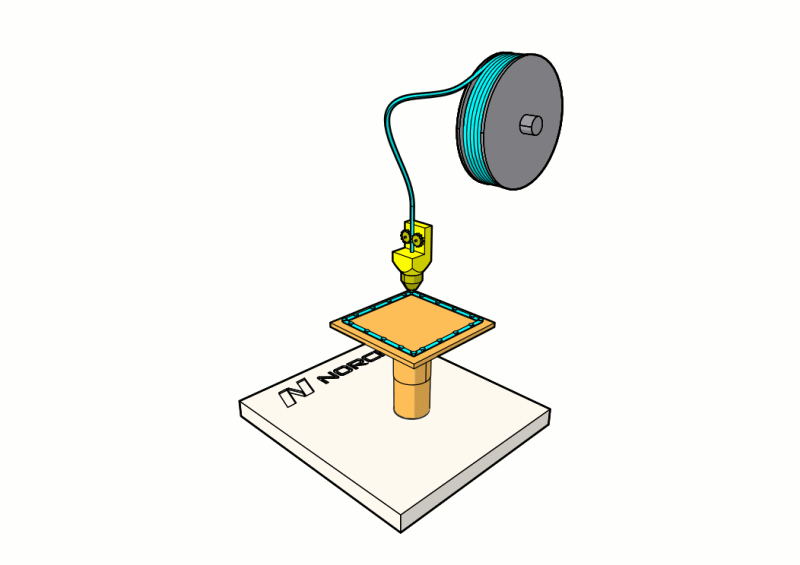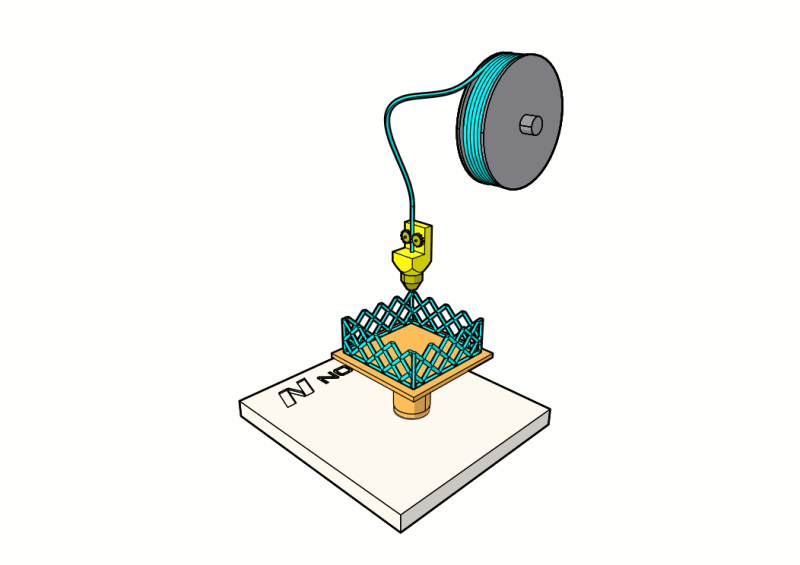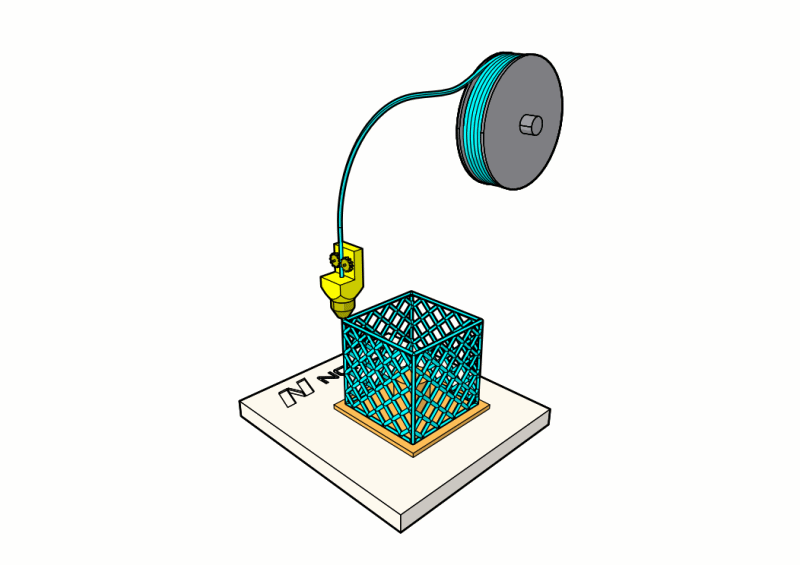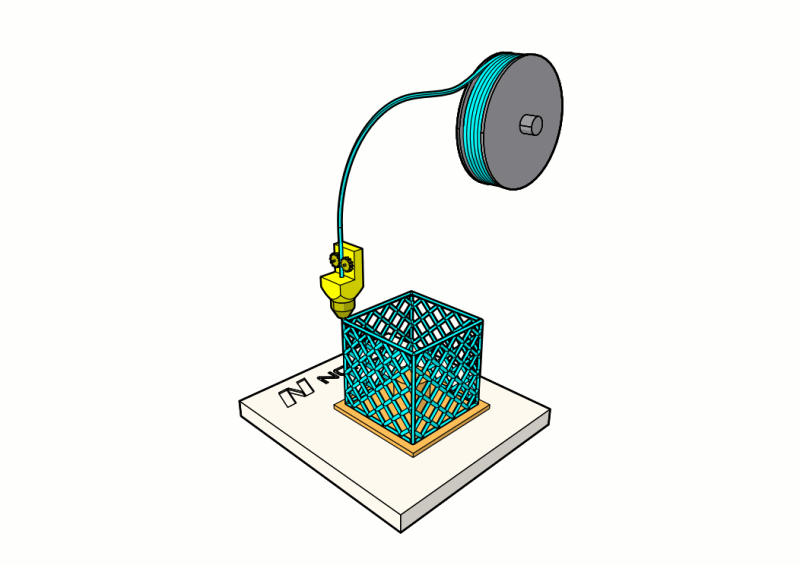
The 3D printer slices the 3D model into several cross sections and prints them layer by layer. At Norck, we offer the following 3D printing methods:
1. Plastic 3D printing: Multiple 3D printing methods produce a plastic part, such as FDM, SLA, SLS, polyjet, and carbon DLS.
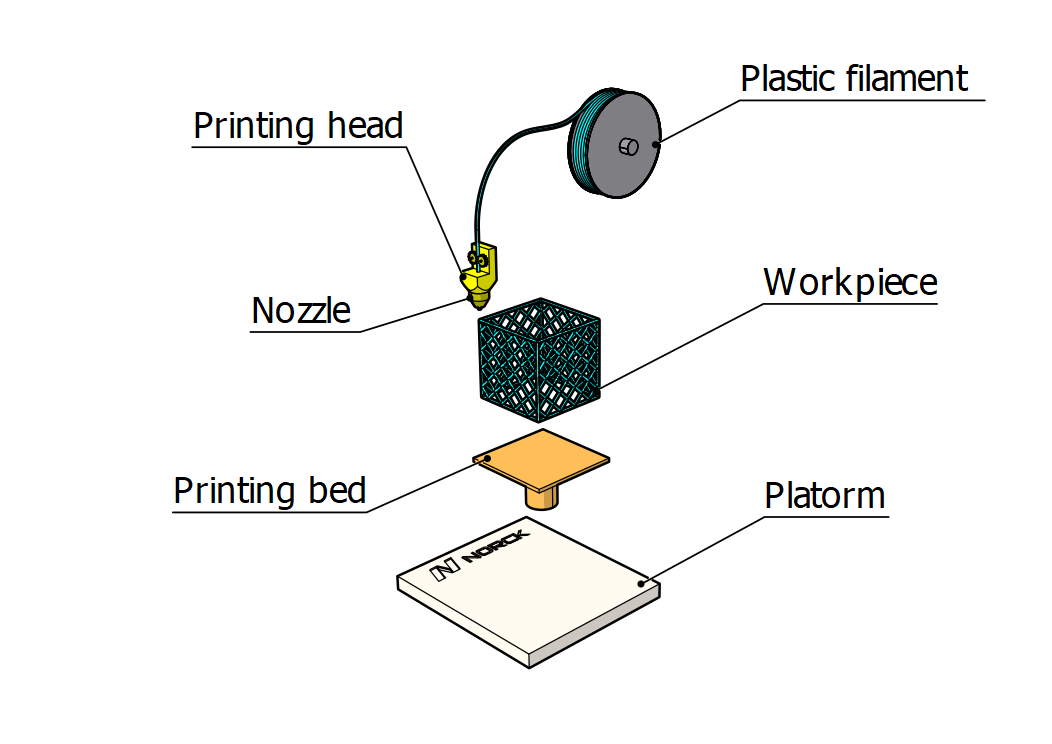
2. Fused deposition modeling (FDM): FDM is the most popular and most cost-effective of the 3D printing processes. It uses a filament of a thermoplastic material such as PLA and ABS. The filament passes through a hot nozzle that melts it, and using a computer-controlled system, the nozzle moves along two axes and deposits the melted material on a platform. When a whole layer of the desired shape is deposited, the platform moves down to deposit the next layer. Once the 3D printed model is finished, it can be removed from the platform. Post-processing might be required to remove any excess material and burrs or to smooth surfaces.
- Most used materials:
• Polylactic acid (PLA)
• Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
• Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
• Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
• Poly-ether-ketone (PEEK)
• Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)
3. HP Multi Jet Fusion: It is a 3D printing method invented by Hewlett-Packard. In HP multi-fusion jet. Each layer of powder material is deposited upon a print bed by a material depositing unit. Then a thermal unit moves across the print bed to deposit a fusing agent and detailing agent. The fusing agent is deposited where powder particles should fuse, and the detailing agent is applied to the contour to help cool the part. The thermal units also contain infrared light to merge the particles and form the desired shape.
Once the 3D printed model is finished, it should cool down before being removed from the platform. Post-processing might be required to remove any excess material and burrs or to smooth surfaces.
-Most used materials:
• PA 11
• PA 12
• PA 12 40% GF
• PP
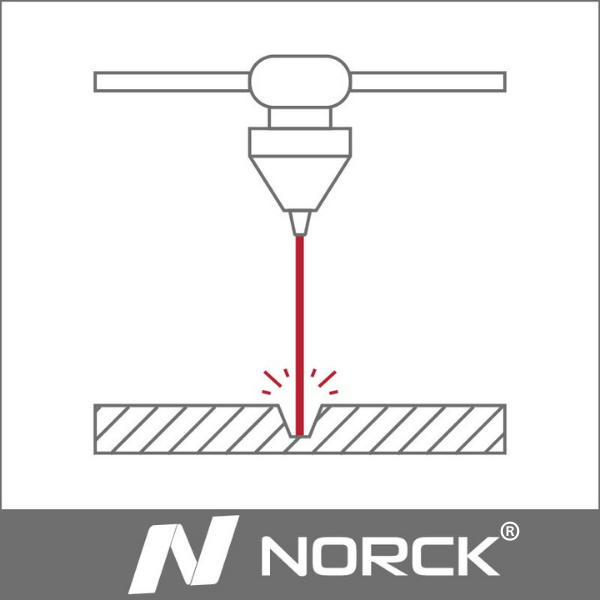
4. Selective laser sintering (SLS): Selective laser sintering is an additive manufacturing process in which particles from a bed of plastic powder are fused to produce parts and assemblies. Each layer of powder material is deposited upon a print bed by a material depositing unit. Then a laser beam is generated and oriented by a rotating mirror to fuse powder particles.
Once the 3D printed model is finished, it should cool down before being removed from the platform. Post-processing might be required to remove any excess material and burrs or to smooth surfaces.
- Most used materials:
• PA 11
• PA 12
• PA GF
• PA FR
• Ceramics
• Glass
5. Stereolithography (SLA): It is a process in which a UV-sensitive resin is cured to form parts and assemblies with a laser. The laser generator projects a cross-section on a transparent window under the resin bath, which will solidify the UV-sensitive resin. The hardened resin will be attached to a platform and pulled up. The platform will be lowered again for the next layer, which will be attached to the solidified layer.
Once the 3D printed model is finished, it can be removed from the platform and submerged in isopropyl alcohol to remove any excessive resin. Then the model gets exposed to passive UV light.
- Most used materials:
• Polycarbonate-like Resin
• Polypropylene-like resin)
6. Polyjet: The polyjet process is similar to inkjet printing. The nozzle moves along two axes and jets liquid UV-sensitive photopolymer onto a platform. Next, UV light is used to solidify the deposited layer of photopolymer. When a whole layer of the desired shape is deposited, the platform moves down to deposit the next layer. If the part requires support structure, drops of wax are jetted to support the model, which will be removed later by heating the printed piece.
Once the 3D printed model is finished, it can be removed from the platform. Post-processing might be required to remove any excess material and burrs or to smooth surfaces.
- Most used materials:
• Polycarbonate-like Resin
• polypropylene-like resin
• Rubber-like resin
7. Carbon DLS: Carbon Digital Light Synthesis is a 3D printing process that uses a UV-sensitive resin to produce the desired model. In this process, a light source is used to project UV cross sections of a 3D model on a window, which transforms the resin.
- Most used materials:
• Elastomeric resin
• Flexible resin
• Rigid resin
• Silicone
• Cyanate ester
• Urethane Methacrylate
• Epoxy
• Medical ABS-like
8. Metal 3D printing: At Norck, we can print with metallic materials such as Stainless steel, Cobalt, and Inconel. The process that we use is DMLS.
9. Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS): Like SLS, direct metal laser sintering is a process that uses a laser to form the desired shape by fusing particles of metallic powder instead of plastic. In this process, a roller deposits layers of powder metal on the print bed, then the laser fuses powder metal particles on each layer.
- Most used materials:
• Titanium
• Steel
• Stainless steel
• Aluminum
• Nickel
• Cobalt
• Copper
• Inconel
• Gold
• Platinum
• Silver
10. Vapor smoothing: It is a post-process for 3D printed parts with a coarse surface finish to smooth and enhance their mechanical and visual aspects. Vapor smoothing uses chemical vapor solvents to smooth the 3D-printed part by melting the surface.
- It is used with most polymers and elastomers, such as:
• ABS
• PP
• PC
• PLA
• PETG
• PA 12
• ASA
Parts and assemblies should follow specific design rules to be printed correctly. Norck offers engineering services that will help you confirm your design for 3D printing.


 English
English